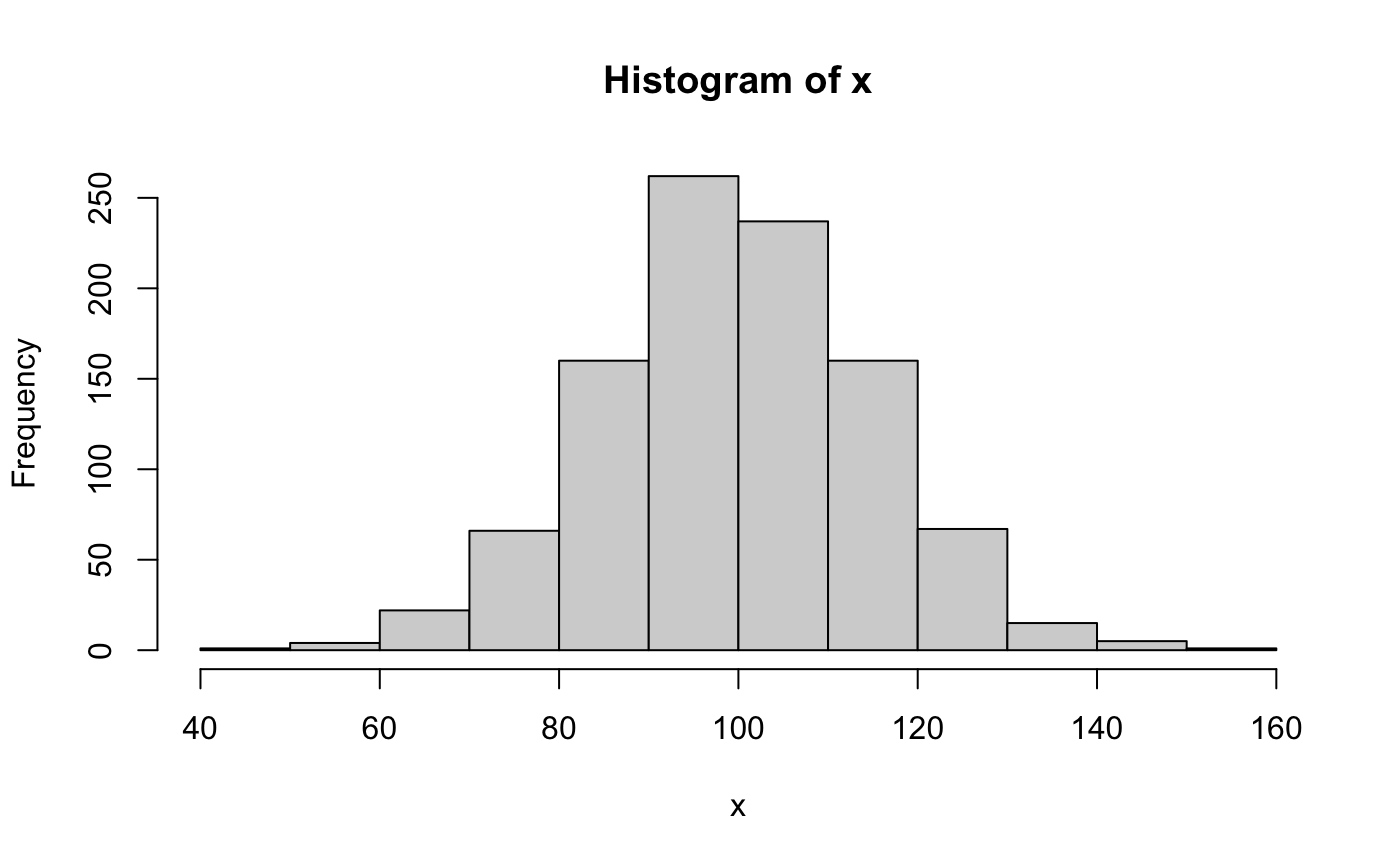
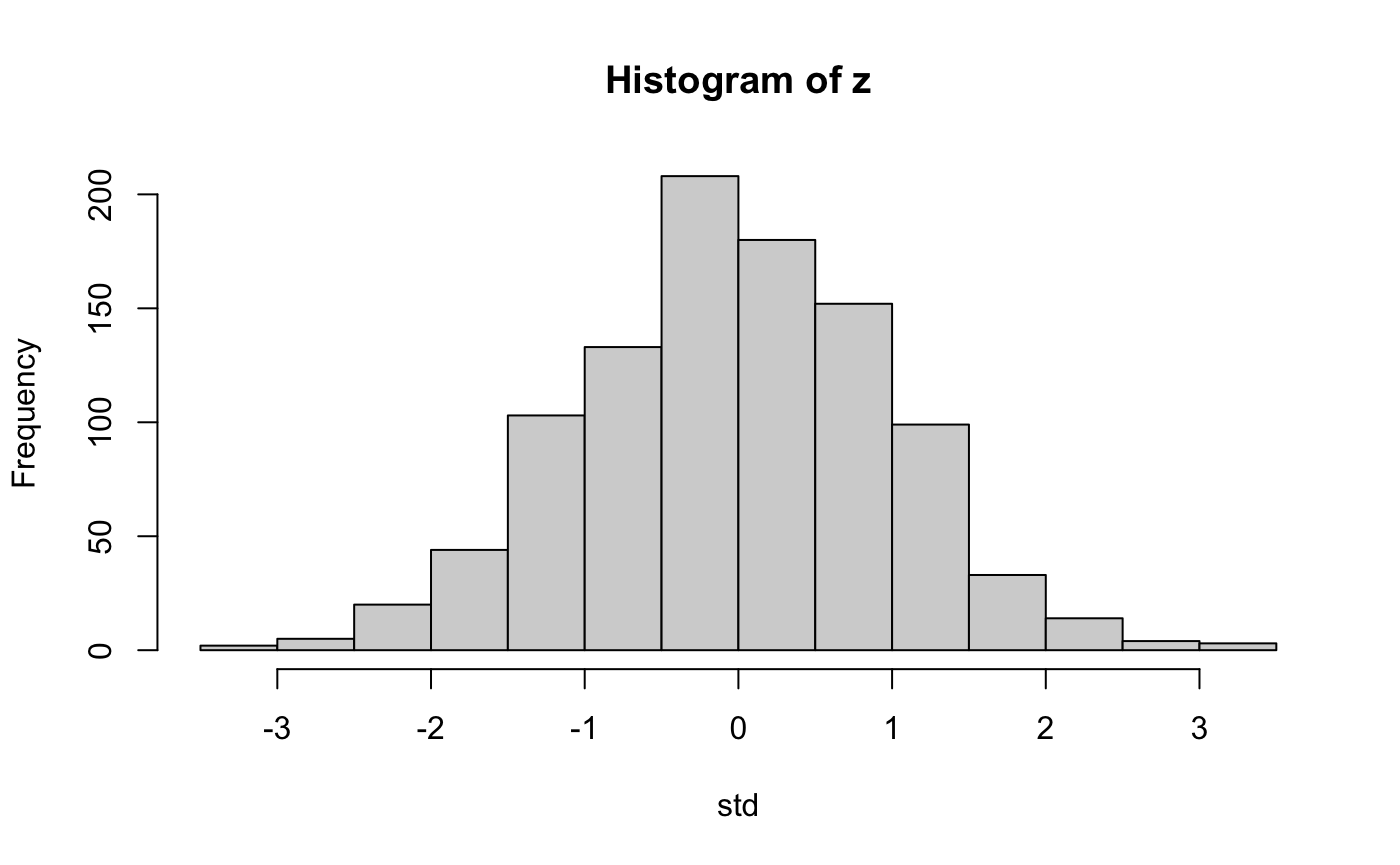
In statistics, a \(z\)-score (standard score) is a signed value that indicates the number of standard deviations by which a data point is above or below the mean. A positive value indicates that the data point is above the mean. A negative value indicates that the data point is below the mean. It is calculated by subtracting the mean \(\left(\mu\right)\) from the data point \(\left(x\right)\) and dividing by the standard deviation \(\left(\sigma = \sqrt{\sigma^2}\right)\).